Digital lending refers to the process of providing financial loans and credit services through digital platforms, usually using online technology and data analytics. It involves the use of digital channels, such as websites, mobile apps, and online portals, to facilitate the loan application, approval, disbursement, and repayment processes. Digital lending has gained popularity in recent years due to the rapid advancements in technology and the increasing adoption of online and mobile banking services.
The history of digital lending dates to the early days of the internet and the emergence of online financial services. Here are some key milestones in the evolution of digital lending:
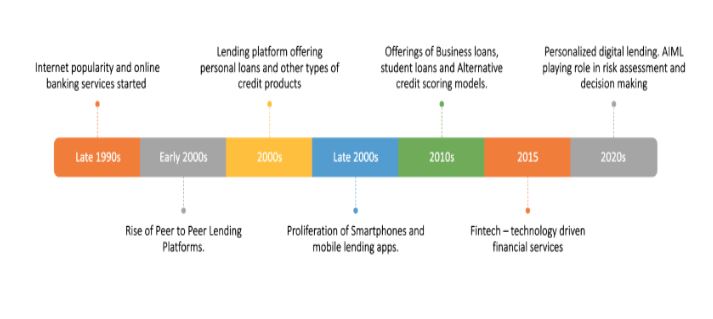
- Late 1990s: The internet gained popularity, and financial institutions started exploring online banking services. However, the lending process was still largely paper-based and required borrowers to visit physical branches.
- Early 2000s: The rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms marked a significant shift in the lending landscape. The first notable P2P lending platform, Zopa, was founded in the UK in 2005. It allowed individuals to lend and borrow money directly from each other through an online marketplace.
- Mid-2000s: Online lending platforms began to emerge, offering personal loans and other types of credit products online. These platforms simplified the loan application process and used technology to streamline credit assessments and loan approvals.
- Late 2000s: With the proliferation of smartphones and mobile internet access, mobile lending apps started gaining popularity. Borrowers could now apply for loans and manage their accounts directly from their mobile devices.
- 2010s: The digital lending industry continued to grow rapidly. New players entered the market, and existing platforms expanded their offerings to include business loans, student loans, and more. Online lending became more sophisticated with the use of data analytics and alternative credit scoring models.
- 2015: The term “fintech” (short for financial technology) became widely used to describe the growing sector of technology-driven financial services, including digital lending.
- 2020s: As technology continued to advance, digital lending became more personalized and accessible. Artificial intelligence and machine learning played an increasingly significant role in credit risk assessment and decision-making.
Key features and benefits of digital lending include:
Convenience
Digital lending offers a more convenient and streamlined loan application process, enabling borrowers to apply for loans from the comfort of their homes or through their mobile devices.
Speed
The use of digital platforms allows for faster loan processing, reducing the time it takes to evaluate applications, assess creditworthiness, and disburse funds.
Accessibility
Digital lending platforms can reach a broader audience, including individuals in remote areas who may have limited access to traditional banking services.
Data-driven decision-making
Digital lending leverages data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms to assess credit risk, determine loan eligibility, and set personalized interest rates.
Enhanced customer experience
Borrowers can access real-time information, track their loan status, and receive personalized loan offers, improving overall customer satisfaction.
Lower operational costs
Digital lending reduces the need for physical infrastructure and paperwork, resulting in cost savings for lenders, which can sometimes be passed on to borrowers in the form of lower interest rates or fees.
The future of digital lending is likely to be shaped by ongoing technological advancements, evolving customer preferences, and regulatory changes.
Key trends, challenges, and opportunities that may define the future of digital lending:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
As AI and machine learning continue to improve, they will play an increasingly crucial role in credit risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer service. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to make more accurate lending decisions and offer personalized loan products based on individual creditworthiness and financial behavior.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize digital lending by providing a secure and transparent way to manage loan transactions, verify identities, and streamline the entire lending process. Smart contracts on blockchain can automate loan agreements, reducing administrative costs and improving efficiency.
Open banking
Open banking initiatives promote data sharing between financial institutions and third-party service providers. This can lead to more comprehensive credit assessments by accessing a borrower’s financial data from multiple sources, making lending decisions more accurate and inclusive.
Mobile-first approach
With the increasing use of smartphones and mobile apps, digital lending is likely to shift further towards a mobile-first approach. Lenders will focus on providing seamless and user-friendly loan experiences through mobile applications.
Integration with e-commerce and retail
We may see more integration of lending services with e-commerce platforms and retail websites. “Buy now, pay later” options and other instant financing solutions could become more prevalent.
Financial inclusion
Digital lending has the potential to address the needs of underserved populations and promote financial inclusion. By using alternative data sources and innovative credit assessment models, lenders can extend credit to those with limited or no credit history.
Data privacy and security
As more personal and financial data is collected and processed in digital lending, ensuring data privacy and security will remain a significant challenge. Striking a balance between data access for better credit assessments and protecting consumer information will be crucial.
Regulatory landscape
The digital lending industry will be subject to evolving regulatory frameworks. Stricter regulations may impact lending practices, compliance requirements, and interest rate capping, which can influence the profitability and viability of digital lending businesses.
Competition and market consolidation
As digital lending becomes more popular, the industry will likely see increased competition, leading to potential market consolidation. Larger, established players may acquire smaller fintech firms, or partnerships between traditional banks and fintech’s emerge.
Cybersecurity threats
With the rise in digital transactions, cyber threats and financial fraud are expected to increase. Lenders will need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect their platforms and customers’ sensitive data.
In summary, the future of digital lending holds great promise, especially in terms of financial inclusion, efficiency, and personalized services. However, challenges related to data security, regulatory compliance, and competition will need to be addressed effectively to realize the full potential of digital lending in the coming years.


