The growth of modern IT environments has been exponential and remarkable, with an ever-increasing amount of data being generated, stored, and processed. As in any period, here as well growth brings in new challenges and new opportunities in response to these growing complexities. This insightful article delves deep into data fabric and its evolution.
Data management and integrations continues and adapts to the changing data landscape, including emerging technologies and increasing data complexities. Thus, bringing in need of a unified and flexible architecture that enables seamless data access, sharing, and management across different data sources and environments.
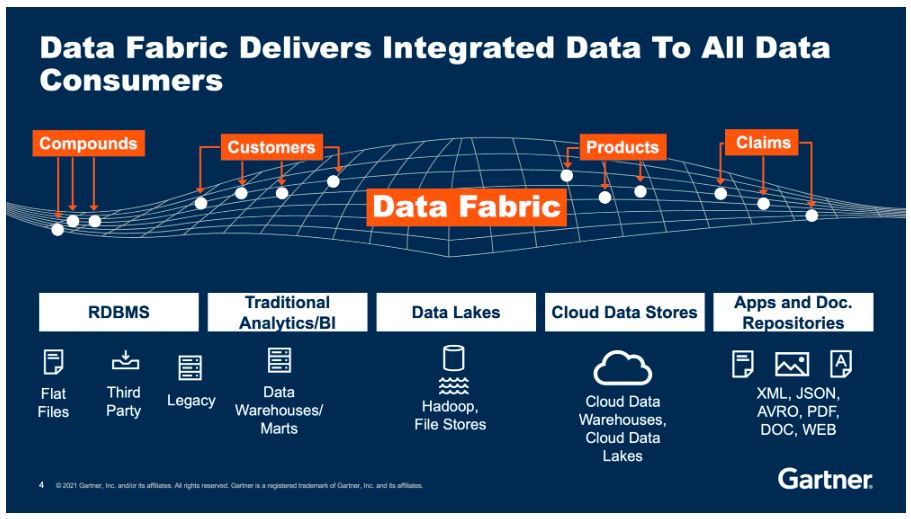
Thus, brings in the concept of “Data fabric” in the field of data management and integration. It’s a unified and flexible architecture that enables seamless data access, sharing, and management across different data sources and environments.
The evolution of data fabric has been influenced by the changing landscape of data management and the need for more agile and scalable solutions.
The evolution of data fabric has been influenced by the changing landscape of data management and the need for more agile and scalable solutions.
Evolution of data fabric
Traditional data integration
In the past, organizations relied on traditional data integration approaches, such as Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) and Enterprise Service Buses (ESBs), to consolidate and transfer data between systems. While these methods served their purpose, they often involved batch processing and point-to-point connections, making them less suitable for real-time and complex data scenarios.
Rise of data virtualization
Data virtualization emerged as a solution to the limitations of traditional data integration methods. It allows organizations to create a virtual layer that abstracts data from various sources, providing a unified view of the data without physically moving it. This approach improved data access and reduced data redundancy, enabling faster insights and analytics.
Growth of big data and cloud computing
The proliferation of big data and the adoption of cloud computing presented new challenges and opportunities in data management. Data fabric solutions evolved to handle the growing volume, variety, and velocity of data generated by diverse sources, including social media, IoT devices, and cloud-based applications.
Need for real-time data processing
As businesses sought to gain real-time insights and respond to rapidly changing market conditions, data fabric solutions had to incorporate real-time data processing capabilities. These solutions often use stream processing frameworks to handle data in motion and ensure data freshness and relevance.
Hybrid and multi-cloud environments
With the increasing adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies, data fabric solutions expanded their capabilities to seamlessly integrate and manage data across different cloud providers and on-premises data centers. This enabled organizations to maintain data consistency and accessibility in complex distributed environments.
Data governance and security
As data privacy and security became paramount concerns, data fabric solutions incorporated robust data governance features. These include data lineage, data quality monitoring, and access control mechanisms to ensure compliance with regulations and protect sensitive data.
AI and Machine Learning integration
Data fabric solutions have started integrating with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities. By leveraging AI algorithms, data fabric can optimize data movement, automate data discovery, and enhance data quality, thereby providing more intelligent and efficient data management.
Semantics and data catalogs
The evolution of data fabric also involves incorporating semantic capabilities and data catalogs. These features enable better data discovery and understanding by providing context and meaning to data assets, making it easier for users to find and utilize relevant data.
Data fabric architecture provides a centralized, connected layer of integrated data that democratizes cross-company data access. A well designed data fabric architecture is modular and supports massive scale, distributed multi-cloud, on-premises, and hybrid deployment.
Complete architecture
Data fabric architecture consists of six layers: data management, data ingestion, data processing, data orchestration, data consumption, and data fabric platform. These six layers include the following:
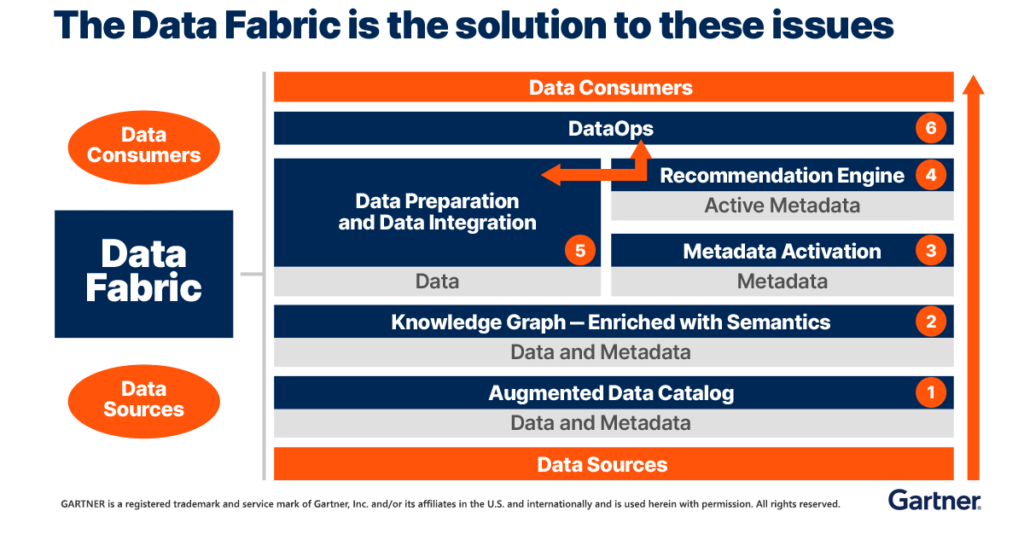
- Data Management layer: This is responsible for data governance and security of data. It defines and enforces data policies, rules, and standards, and ensures data quality, lineage, and provenance.
- Data Ingestion layer: This layer begins to stitch cloud data together, finding connections between structured and unstructured data from various sources, such as legacy systems, data lakes, data warehouses, SQL databases, and apps. It supports different integration styles, such as batch, streaming, virtualization, and transformation.
- Data Processing layer: The data processing layer refines the raw data into actionable insights. It applies advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, to extract value from the data.
- Data Orchestration layer: This layer coordinates the execution of data workflows across different environments and platforms. It leverages APIs and microservices to enable seamless data movement and communication.
- Data Ccnsumption layer: This layer enables self-service data consumption for various users and applications. It provides a marketplace where users can find, collaborate, and access high-quality data. It also supports different delivery modes, such as dashboards, reports, visualizations, and alerts.
- Data Fabric platform: This is the underlying infrastructure that supports the data fabric architecture. It is a composable and scalable platform that leverages cloud-native technologies, such as containers, Kubernetes, and serverless computing.
Data fabric architecture is key to modernizing data management and integration in an increasingly diverse, distributed, and complex environment. It can help organizations achieve data agility, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and drive innovation.
Data fabric is expected to grow as more organizations realize the benefits of using a data fabric approach to simplify their data access and consumption. According to Gartner, by 2025:
- 65% of organizations will have shifted from traditional integration platforms to a suite of cloud services that enable them to implement a composable enterprise.
- 50% of organizations will have adopted a cloud-native or hybrid integration platform as a service (iPaaS) as their primary means for application integration.
- 40% of organizations will have implemented at least one AI-enabled automation project involving IT operations.


